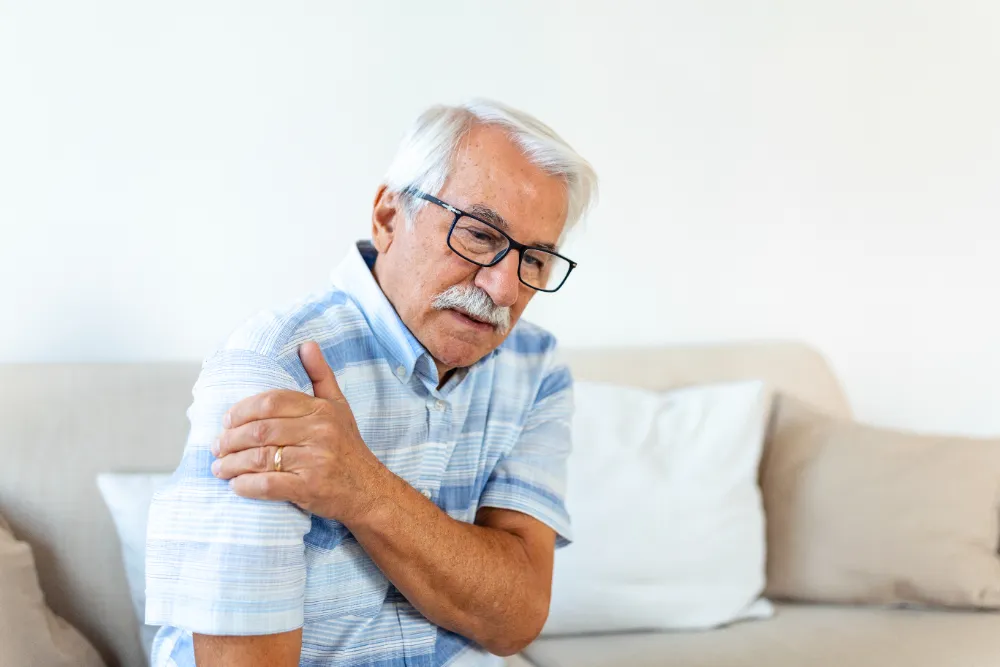
Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis, affecting around one in six people in Canada. It is a progressive degenerative joint disease where the joint cartilage, the protective layer between two bones breaks down and wears away, leading to bones directly rub and grind against each other. Overtime, the accumulation of damage will lead to stiffness and pain, as well as a loss of function of the joint.
Causes
Although more likely to affect the elderly, osteoarthritis can occur at any age. It is a result of overuse of joints and the accumulation of wear-and-tear, which is often the consequence of aging, obesity, works of high physical demands, and sports such as athlete or dancer. It can also be exacerbated or caused by injuries such as dislocations, ligamental injuries and torn cartilage as well. Genetic and sex can also play a role in the risk of osteoarthritis.
Symptoms
Treatment
- Physical activity and light-impact exercise
It is often thought that arthritis needs to limit their movement. However, not enough physical activity can lead to muscle weakness, which in turn worsens joint pain and stiffness.
Aside from lessening existing symptoms, daily light or moderate physical activity strengthens the muscles, increase blood flow to joint and help promote joint regeneration. Overtime, slowing or even preventing further progression, maintain and improve the mobility of the joint. - Maintain a healthy weight
While there are no clear-cut definition of healthy body or healthy weight, obesity is found to be a risk factor for osteoarthritis. Excess body weight on the load-bearing joints leads to an increased wear-and-tear, which in turn quickens the process of osteoarthritis development. Reducing excess weight can help reduce straining and pain, as well as slowing progression, even a modest amounts of weight loss – 10-20 lbs – can be beneficial. - Antiinflammatory Diet
As osteoarthritis involves inflammatory of the joint, a diet focusing on reducing inflammation can provide symptom relieve and delay progression. Antiinflammatory diet emphasizes whole foods, fish, leafy greens, nuts and seeds, while decrease or eliminate the consumption of processed foods, simple sugars and simple carbohydrates, red meat, as well as any food sensitivities. - Topical applications
- Castor oil
The antiinflammatory effects of castor oil when applied topically can reduce the symptoms of pain in arthritic joints. Apply a thin layer of castor oil on affected joint, cover with a thin cloth to prevent sticking to other surfaces, use a heat pad or other heat application for 20 minutes to achieve optimal benefit.
*Important note – castor oil is very sticky, so use a cloth or old towels/t-shirt for ease of clean-up. Castor oil is NOT to be taken internally. - Heat and coldHeat applications on painful joints relaxes tight muscles and increase circulation and metabolize waste products quicker. It is best used for chronic joint pains where there are no signs of inflammation or flare of acute injury or aggravation.
Cold applications decrease blood flow to reduce swelling and slows transmission of pain signals, slowing or inhibiting inflammatory response. It is best for pain and swelling after exercise or during the first 24-72 hours after a flare or injury.
After the initial 48-72 hours, try alternating hot and cold applications with the hot vs cold time on a 3:1 ratio (eg 3 minutes of hot application, then switch to cold application for 1 minute). Continue the alternation for 15-20 minutes, ending in cold application.
*Note – caution on not using temperatures that can burn the skin, use a thin cloth or paper towel on the packs for protection.
- Castor oil
- Acupuncture
It has been found that acupuncture provides anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects for osteoarthritic joints compared to placebo, providing significant reduction in pain intensity, functional mobility, and overall quality of life.
Osteoarthritis can greatly impede on the quality of life, Naturopathic Doctors can provide an individualized and comprehensive plan to support patients using various supplements and modalities.