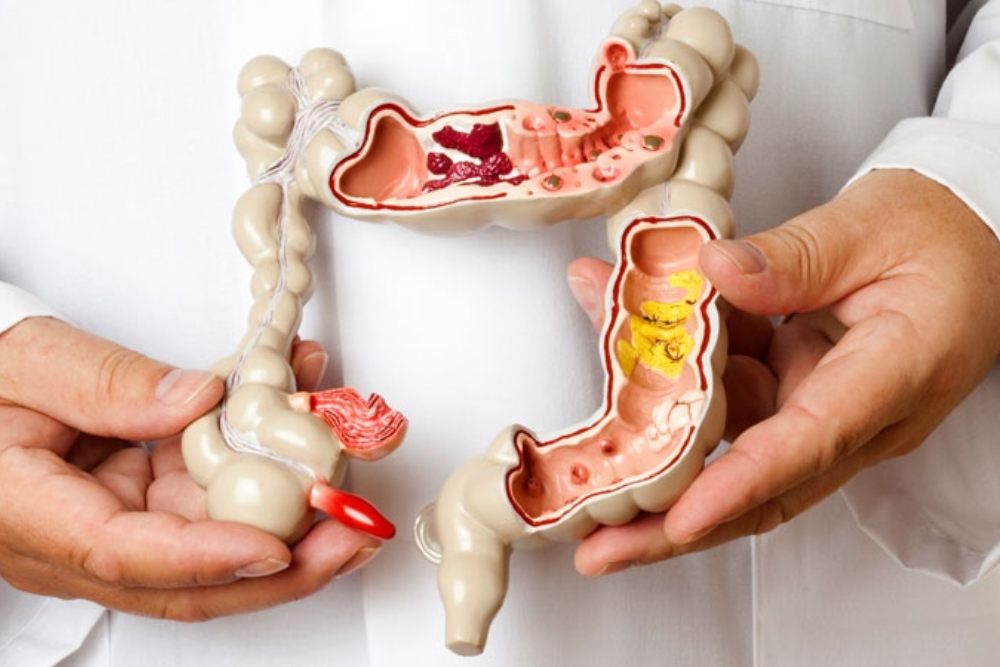
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a common digestive disorder that affects the stomach and intestines. While it can cause significant discomfort, it does not lead to permanent damage. IBS is a functional gastrointestinal disorder, meaning that although the gut appears normal, it doesn’t work as it should. It can affect people of all ages, though it is more common in women and younger individuals. Proper management is crucial for maintaining overall health and quality of life.
Based on bowel patterns, IBS is further classified into subtypes of:
IBS is a diagnosis of exclusion, made after ruling out conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), celiac disease, and infections. Diagnosis is confirmed using the ROME IV criteria:
IBS is often linked to several underlying factors such as food sensitivities, bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), overactive nervous systems, gut inflammations or leaky gut. Some testings may be included to rule out potential causes:
Many are told to simply “live with” IBS and manage with fibre supplements and stress reduction, often with limited success. Addressing the root cause is key to improving long-term health and quality of life.
Dr. Wu, ND, takes a personalized approach to IBS management, including dietary adjustments, supplements, herbs, and lifestyle changes that utilize the 4 Rs of gut health management—Remove, Replace, Reinoculate, and Repair—as outlined in the Areas of Focus. Effective IBS management goes beyond symptom control; it aims to rule out underlying causes, provide long-term relief, resolve gut inflammation, and ultimately restore proper digestive function.
If you’re ready to take the next step toward better digestive health, Dr. Wu is here to help you on your journey.
― dr.sheenawu.nd





Email: [email protected]
Email: [email protected]
© 2025 Dr. Sheena Wu, ND | All rights reserved | Designed & Developed by scaleup42.com